Design (Yelp)Business Review- System Design [HLD]
Design a system like yelp which publishes crowd-sourced reviews about businesses.
Designing a Yelp-like review system requires a robust, scalable, and efficient architecture to handle millions of users and billions of reviews, searches, and interactions.
In this post, we will walk through designing a system that can provide features similar to Yelp, focusing on scalability, low latency, and high availability.
Note: if you see 🚩 dig deeper to come up with an answer that will help you to prepare better.
1. Requirements Gathering
Functional Requirements:
Business Listings: Users can search and view business profiles, including restaurants, shops, and services.
User Reviews: Users can post reviews and rate businesses on a 1-5 star scale.
Search and Filters: Users can search for businesses based on location, category, ratings, and price range.
User Profiles: Each user should have a profile to track reviews, likes, and contributions.
Business Categories: Businesses should be categorized for easy browsing (e.g., restaurants, shopping, services).
Photos: Users can upload pictures of businesses.
🚩 "What other features would you add to improve the user experience for a Yelp-like service?
Non-Functional Requirements:
Scalability: The system should support millions of users and businesses with high volumes of reviews.
Low Latency: Real-time search results and reviews must load quickly.
High Availability: The system should be available 99.99% of the time.
Search Optimization: The system should provide fast, relevant, and personalized search results.
Global Reach: Users should be able to search for businesses from various geographic locations.
🚩Are there any additional non-functional requirements you'd prioritize for scaling to millions of users?
2. Capacity Estimation
Let's assume the following traffic characteristics:
User Base:
Total registered users: 500 million
Daily active users (DAU): 50 million
Reviews per day: 10 million
Average review size: 1 KB
Average photo size: 2 MB
Business Listings:
Total number of businesses: 10 million
Average photos per business: 10
Average business profile size (metadata, description, etc.): 5 KB
Data Transfer Estimation:
Daily reviews: 10 million × 1 KB = 10 GB/day
Daily photo uploads: 5 million × 2 MB = 10 TB/day
Storage Estimation:
Business profile storage: 10 million × 5 KB = 50 GB
Review storage: 1 billion reviews × 1 KB = 1 TB
Photo storage: 100 million photos × 2 MB = 200 TB
Caching is crucial for reducing the load on databases. Popular businesses and frequently searched categories should be cached.
🚩"How would you manage rapid growth?
🚩If the user base grew by 10x overnight, what part of the system would you scale first?
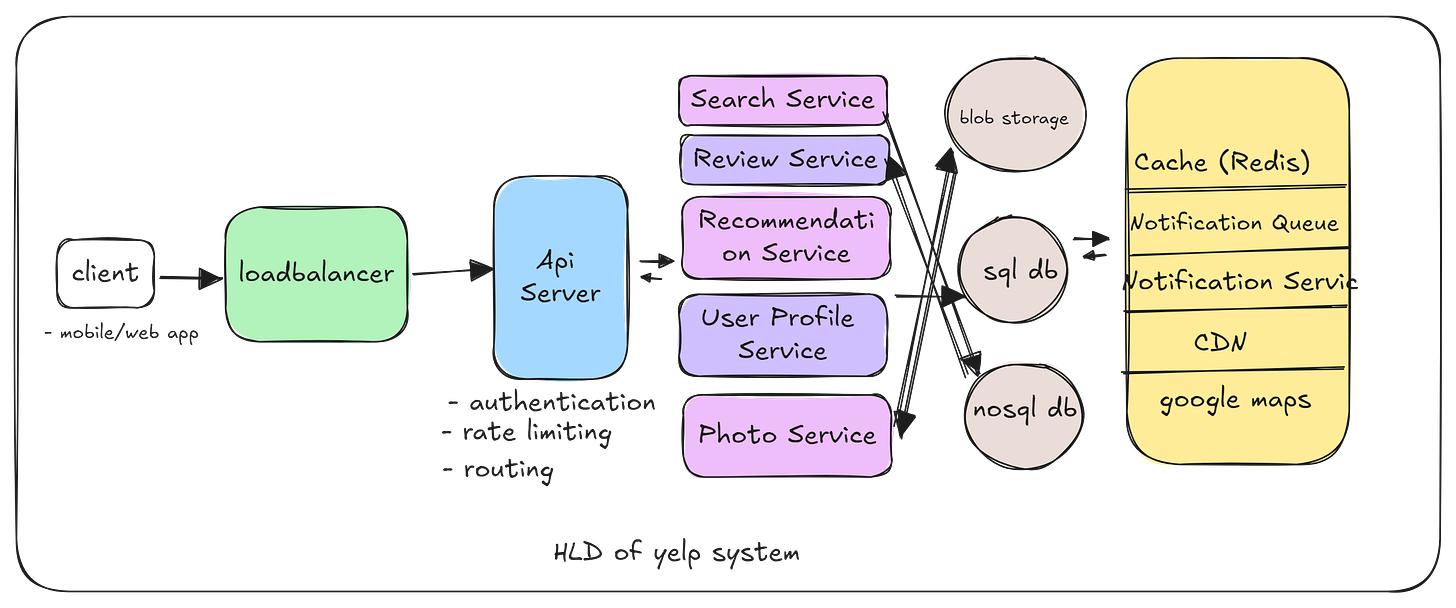
3. High-Level Design
The architecture of a Yelp-like system can be broken down into several core components:
3.1 Client Application
The client application includes mobile, web, and desktop interfaces. It interacts with the backend for searching, browsing businesses, posting reviews, uploading photos, and user profile management.
3.2 Load Balancers
Load Balancers distribute incoming client requests across multiple servers. This prevents server overload and balances traffic efficiently.
3.3 App Servers
App servers handle client requests and pass them on to the appropriate backend services (search, reviews, etc.).
3.4 Services
Search Service: Manages search queries for businesses, categories, and locations, ensuring relevance and ranking of results.
Review Service: Handles the posting, updating, and retrieving of user reviews and ratings for businesses.
Recommendation Service: Provides personalized business suggestions based on the user’s search history and preferences.
User Service: Manages user accounts, profiles, and contributions (reviews, photos).
Photo Service: Handles photo uploads and stores them in a scalable blob storage system.
3.5 Storage
Relational Databases (e.g., MySQL/PostgreSQL): Store structured data like user profiles, business metadata, and reviews.
NoSQL Databases (e.g., MongoDB/DynamoDB): Manage unstructured data such as search indices and user interactions.
Blob Storage (e.g., AWS S3): Store large objects like photos and videos.
Content Delivery Network (CDN): Distributes static content (e.g., photos) globally for low-latency access.
Cache Layer (e.g., Redis): Caches frequently accessed data like popular businesses and top-rated reviews.
3.6 Analytics and Monitoring
Analytics Services track user engagement, system performance, and business popularity generating insights and providing performance monitoring.
We’ve outlined a basic high-level architecture.
🚩How would you approach building this system differently?
🚩Would you use different services or architectures?
🚩How would you use Google maps API for proximity search?